By Gigi Geng
FPS Development History since 1970s
Strictly speaking, FPS: First-person-Shooting Game is a sub-genre of Action Games.
Background
In the 1970s, PC image processing technology is very different from “Famicom”. All kinds of horizontally-scrolling adventure games became dominating on Atari consoles, and PC games at that time were only limited to AVG forms of interactive narrative games.
Origin
Two games have never been seen before on PC platforms: Spasim and Maze War. These two small programs running on professional computers can be regarded as the earliest ancestor of FPS. The poor performance of the PC image processing capability leads to the first pseudo-first-person graphic effect using only vectors and lines. It was unprecedented and seemed impossible at that time because there had never been a first-person perspective in video games, so Maze War was a ground-breaking invention in this genre.
Maze War is the first example of FPS, though this “first FPS” term is loosely interpreted, players navigate the maze using basic movement under the rule that only allows players to move in 90-degree increments. Surprisingly, it is also the first multi-player first-person shooter to have opponent players. It may not fit into today’s gaming mainstream, but few games have had the generational impact like Maze War.
Forming Shape
Battlezone 1980: Atari Platform
Driller 1987: The first game to use the engine Freescape, and Freescape is the first engine.
Rudimental Prototype
February 1st, 1991, ID software was founded, and published the Hovertank 3D in 1991, not a big hit but laid some foundation for the following FPS games.
1992, The Overtaker 3D was published, this game was different from its previous series work and thus shocked the world. Overtaker 3D applied the ray casting technology, one kind of ray tracking technology. The principle is to emit a ray from each line of the screen, if the screen size is 320*240, it will emit 320 rays. Each ray returns the image tile it touched with the nearest object and then draws the content of the tile on top of the pixel row where the rays emit from, (adjusting the size of the image tile based on the distance from the object). This means that instead of rendering the entire map from the beginning, you load the map wherever the player goes, wherever the line of sight is. The limitation of this method is that there is no concept of vertical height, and a 90-degree angle between walls, ceilings and floors can not be pictured in image tiles. The benefit is that it greatly reduced the computational load and in fact, it’s not a real 3D game, but a pseudo 3D effect that was similar to real 3D at that time.
In October 1993 Doom was published.
More refined map rendering technology, more bloody and violent visual expression, exquisite level design and crisp shooting feel.
The biggest highlight of Doom is the introduction of Death Match, a multiplayer matching mode, which has become the most popular mode in all FPS multiplayer games. Doom was also the first FPS to have hidden and explorative gameplay elements, such as armor tenacity, a special setting that also helps lay the foundation for future broader-spectrum FPS.
Imitation and breakthrough: Primitive Age
Doom’s phenomenal success also propelled a faster pace of hardware revolution, which led to a bout of imitation among which some are of poor quality, some are better quality games, The good new is that breakthroughs also follow.
1993 Heretic was published, and produced by Raven Studio, it’s a fantasy FPS and adopted ID software’s Doom engine, bringing FPS to a fantasy world setting.
On certain aspects, Heretic surpassed Doom using an enhanced engine, where players can move view angels up and down, fly and blow away reluctantly by the wind. There is also an inventory system that can store items for proper use at a certain time, including XP boost, stealth and invincible items, time bombs and torches to light up the darkroom.
1995 The Terminator: Future Shock, by Bethesda Softworks.
The concept was far ahead of its time and had a profound impact on all subsequent first-person games. Its achievements includes:
— The first FPS game using mouse control of viewing angles, full view.
—The first FPS game with weaponry on the right side, which has become prevailing at present.
—The first FPS with vehicles.
Open-world outdoor map with most buildings accessible.
Critical Cornerstone: The Golden Age
In May 1996, ID Software published Quake, the first 3D game that truly adopted polygon rendering technology.
In August 1997, GoldenEye was published, bringing excellent console experience and new elements such as multi-mission task, sniper rifle magnifying sight, stealth, etc. which had become the standard setting for most FPS games. This game was able to calculate damage based on the bullet penetration point. The concept of “Headshot” may also be introduced first in this game. (It’s also said that Team Fortress introduced sniper headshots in a game patch in 1996)
November 1998, Delta Force was published, it’s the precursor of the military tactics FPS, pioneered the use of primary and secondary weapons.
November 1998, Half-Life was released, it was developed by the heavily-modified Quake engine, (reportedly 70% of the codes were rewritten). With scripted events, Half-life basically start the new era of narrative FPS. The emergence of Half-life and Valve’s support for Modification led to a gush of high-quality mod games. (Including the famous Counter Strike later)
1999, Unreal and Unreal Tournament, Unreal engine became a mega success later.
December 1999, Quake 3 Arena, was designed for multi-player combat and MMO modes were divided into Free-for-All, Team DeathMatch, Tournament 1v1, etc. Quake 3 first introduced the spectator mode.
November, 2001, Halo series was released, forming the Halo sub-culture community. Special features include:
— a variety of vehicles;
— weapons with distinct functions
— recoverable energy shield (which was unique at the time)
— the ability to carry two weapons
— the ability to melee and throw grenades without switching weapons
— two grenades with different functions
—Character voice
— AI enemies
September 2002, Battlefield was released and had become one of the two mainstream FPS series. BF’s most popular “Conquer” mode originated from WW2-themed BF 1942. As a game featuring big maps, multiple occupations, vehicle driving and multi-player (PC version up to 64 players). BF 1942 spearheaded the shift in FPS from individual heroism to teamwork. Battlefield series presented a style of pseudo-military simulation, combining elements of both a crisp feeling and realism. Starting from BF2, the series begun to introduce a growth system, enabling weapons to unlock as ranks and award ribbons were earned along the game progression, which was widely used later.
October 2003, Call of Duty series was published, adopting a cinematic narrative, the concept of a blood bar (formerly Halo’s recoverable shield)was canceled.
FPS Sub-Genres
FPS genres can be broken up into multiple sub-genres, with each sub-genre composed of different elements, rules, and techniques.
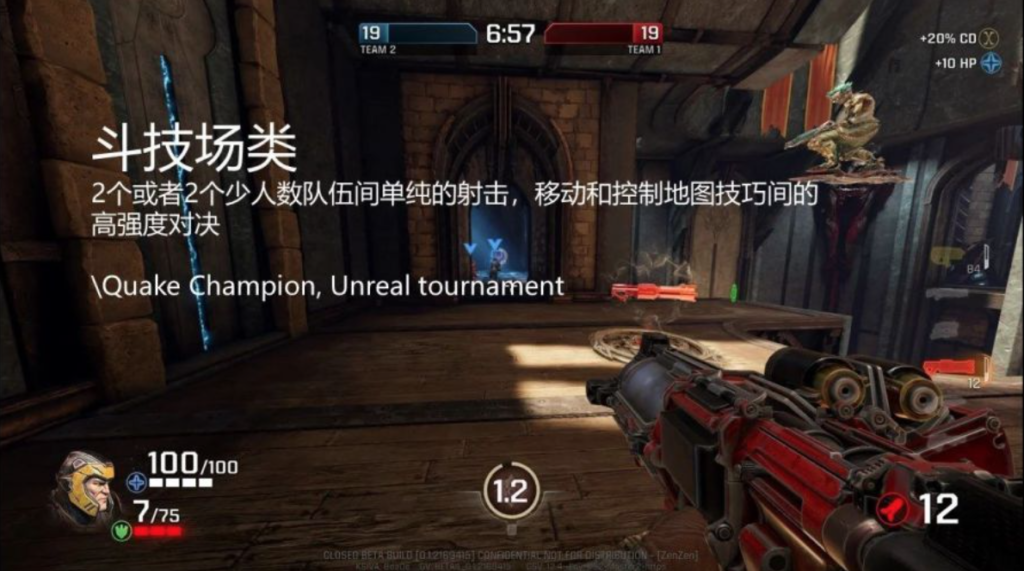
1) Arena Shooter: 2 or less than 2 shooter teams battle with each other, mobility and map control techniques are the key factors in the highly intense duke-out arena.
E.g. Quake Champion, Unreal Tournament
2) Team-based shooter: two teams combat relying on each team member’s personal technics and coordination instead of rich and complicated team battle tactics in a tug-of-war style combat
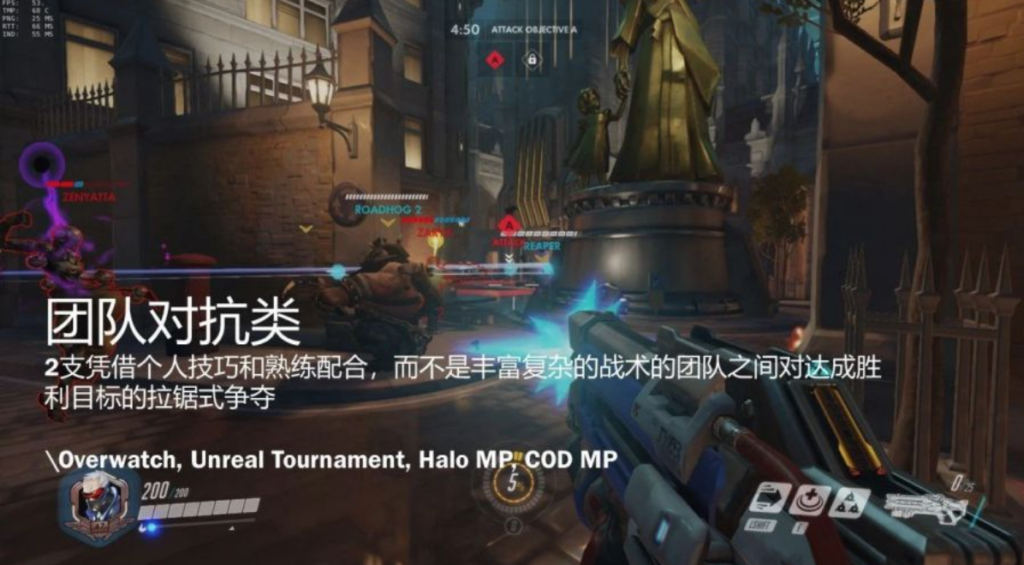
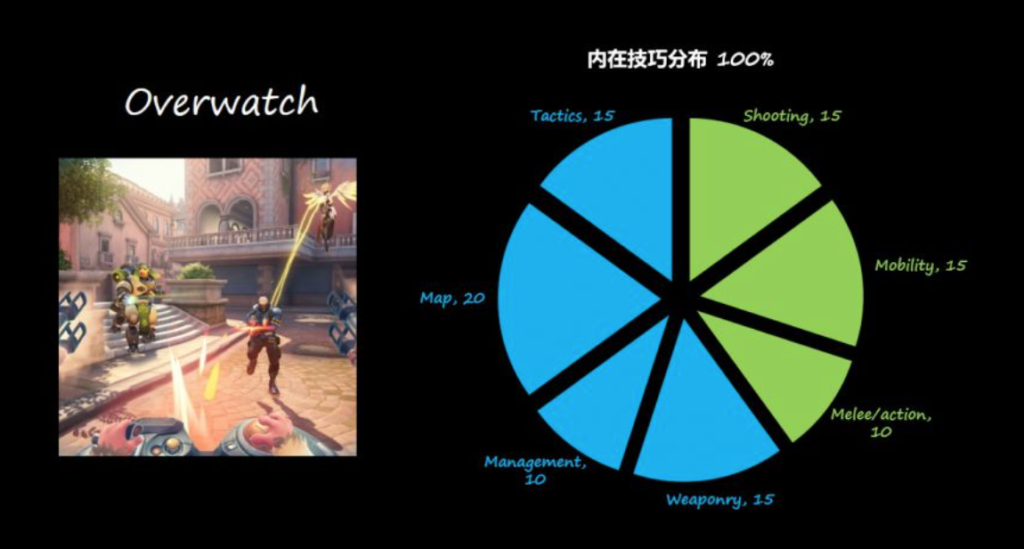
E.g. OverWatch, Unreal Tournament, Halo Multiplayer(MP), COD MP
3) Tactical shooter: Contender teams aim to win against opponents by using crafted team tactics and more cohesive team collaboration
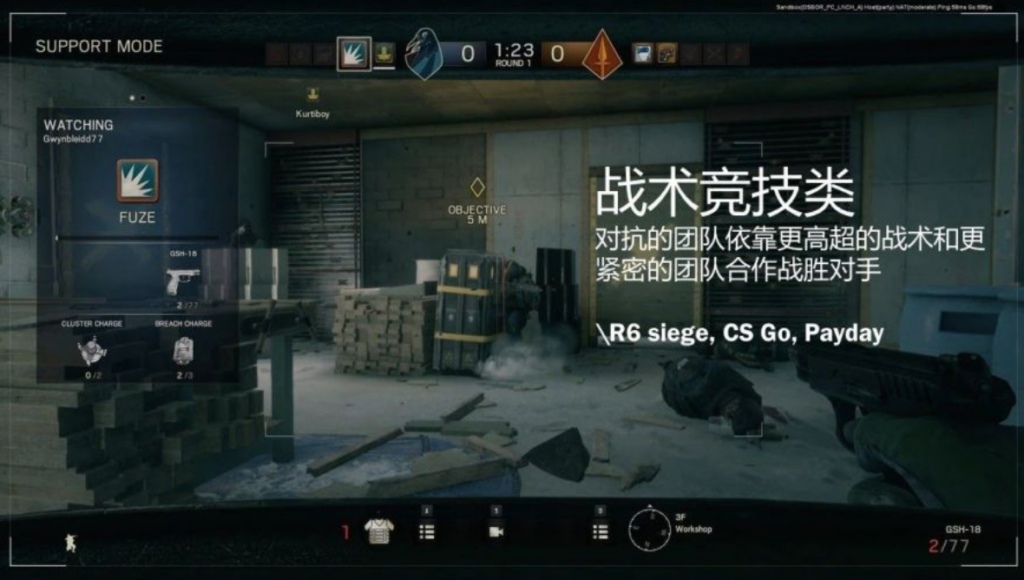
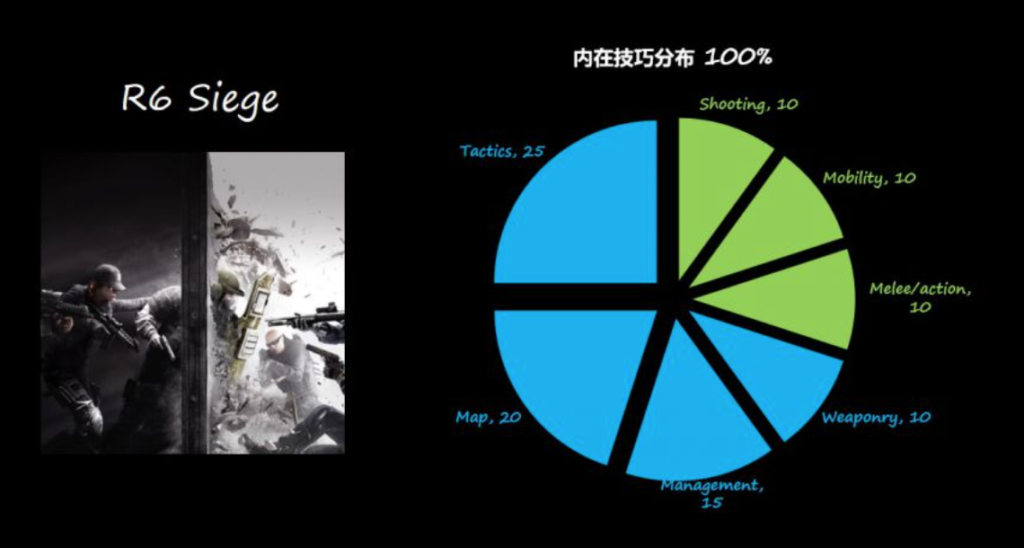
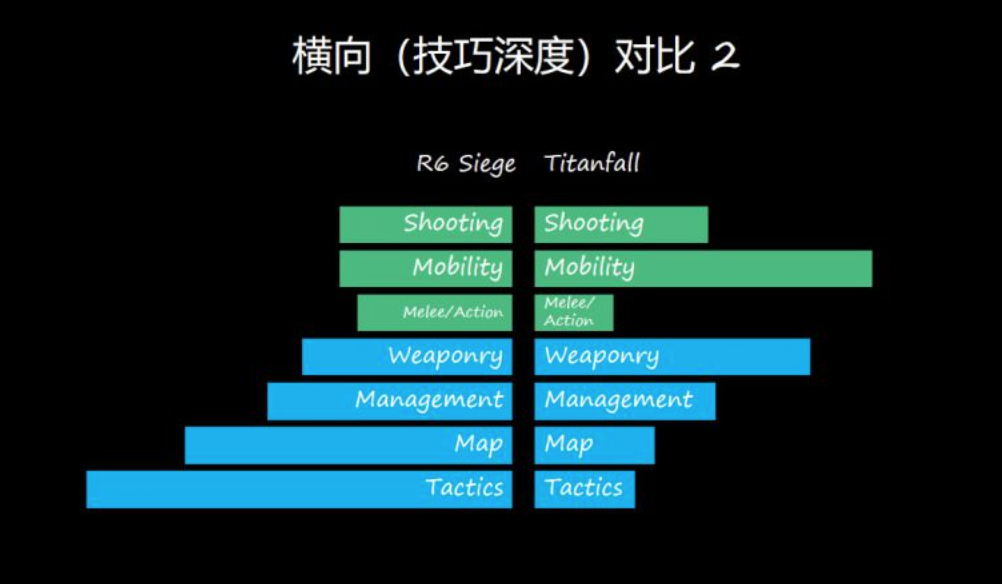
E.g. Rainbow Six Seige, CS:GO, Payday
4) Coop Shooter: requires players to team up and maintain real-time high-level collaboration

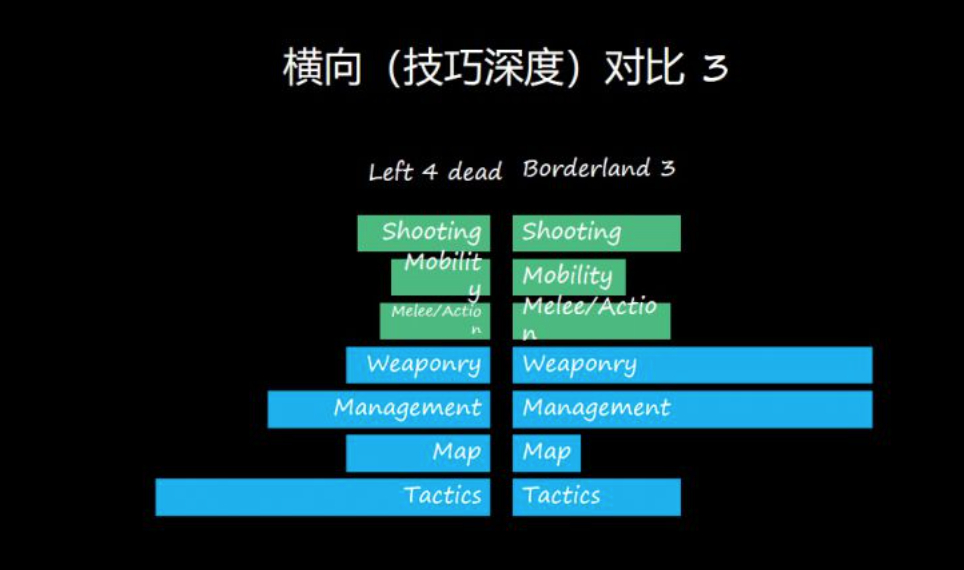
E.g. Left 4 Dead, Destiny, Deep Rock Galactic
5) Military shooter: Game lores are based on real military/war-themed scenarios, weaponry, environment, gameplay and in-field simulation experience

E.g. Call of Duty, Battlefield, Insurgence
6) MMO shooter: Provide an overwhelming battlefield experience through open-world maps and massive online players

E.g. Battlefield, ARMA
7) RPG Shooter: The battle outcome is largely decided by the RPG character’s metrics growth
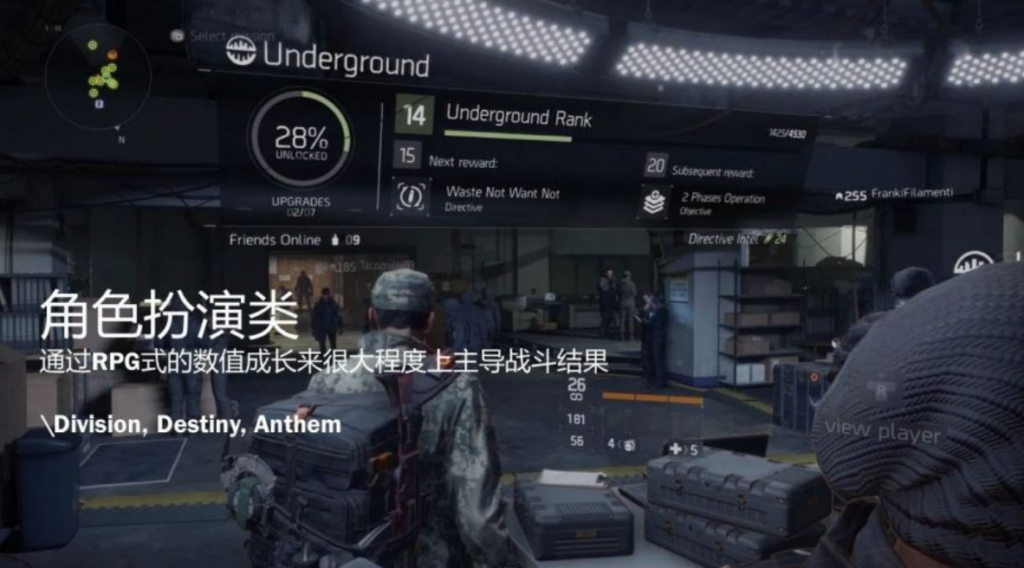
E.g. Division, Destiny
8) Battle Royal shooter: Battlefield ring shrinking mechanism, and special designs for the final survivor

E.g. PUBG, COD Warzone, Apex Legend
9) Alternative shooter: Mixed Mode

Skills are the pivotal factors
Skills are the key factors in defining an FPS sub-genre and player experience, which includes operational skills and intellectual skills.
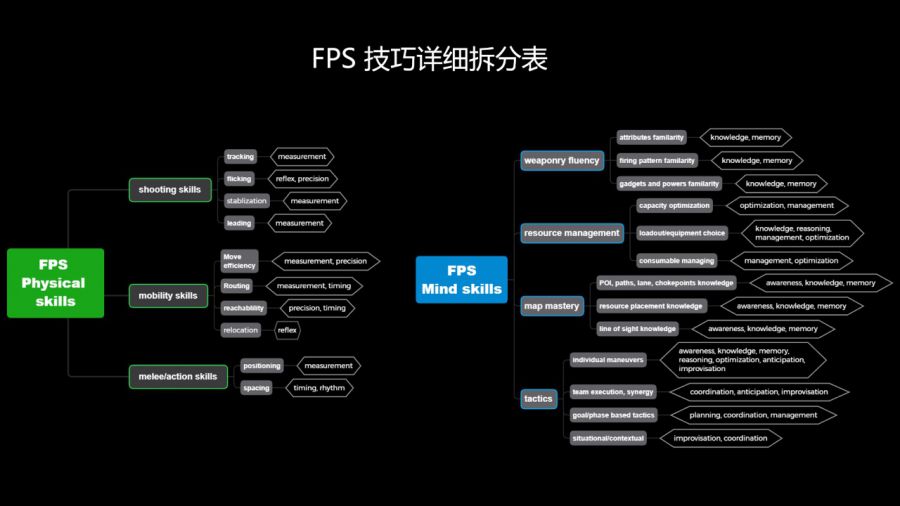
Operational skills are abilities to act accurately, timely, and stably in a game. Core operational skills are common hands-on practices and input skills among multiple game genres. As “eye-brain-hand coordination” is the only path to go through to take any action, intellectual skills unavoidably become the auxiliary condition for physical techniques.
—measurement (move the cursor or joystick constantly)
—accuracy
—timing
—reaction speed
—rhythm
—coordination
Intellectual skills are the player’s ability to find the best strategy to win through interpretation, calculation, inference, and optimization. Core intellectual skills are also part of the common skills widely used among various game genres, involving analytical and logic-based strategizing abilities.
—perceptivity
—comprehension
—Evaluation/reasoning
—management
—optimization/improvement
—memorization
—planning
—coordination
—prediction
—improvised reaction
Other Techniques include:
—Socialization/communication (battle coordination via headset chat )
—psychosocial resilience to pressure
—Patience (towards teammates and for failures )
—Fortitude (when facing crucible challenges)
—Innovation and adaptivity